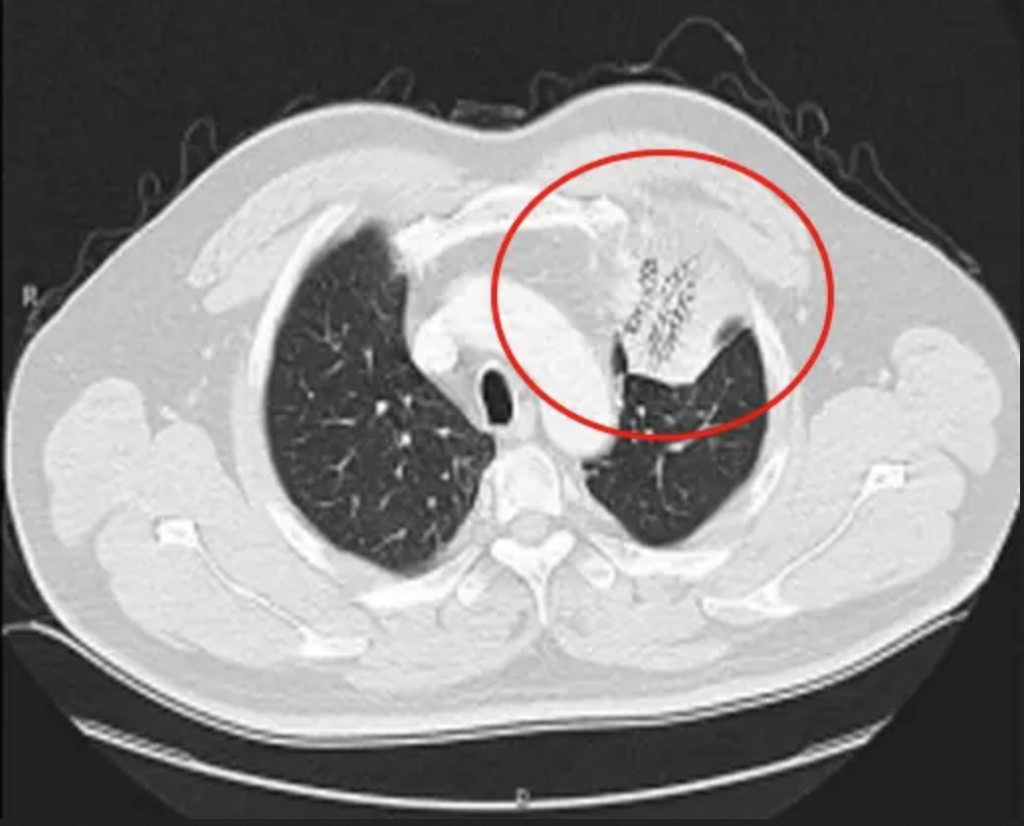
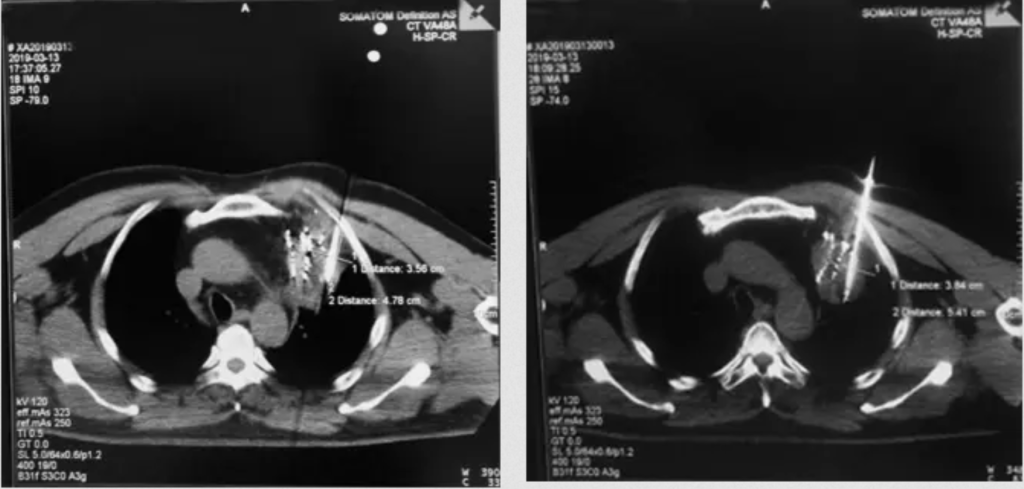
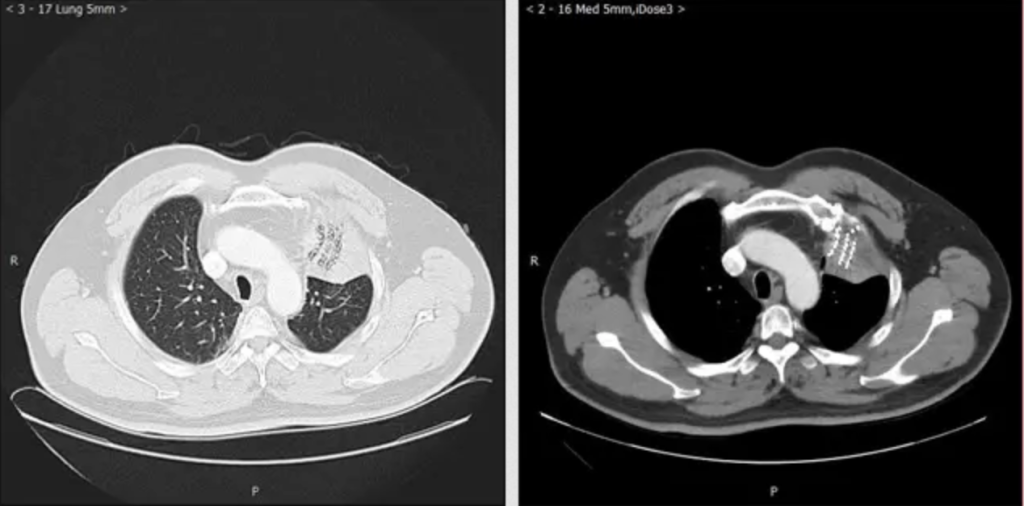
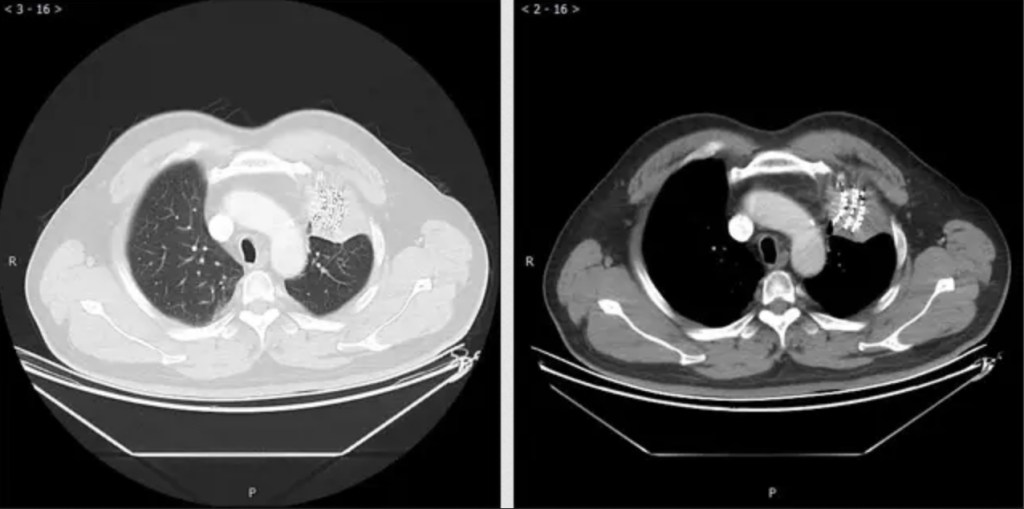
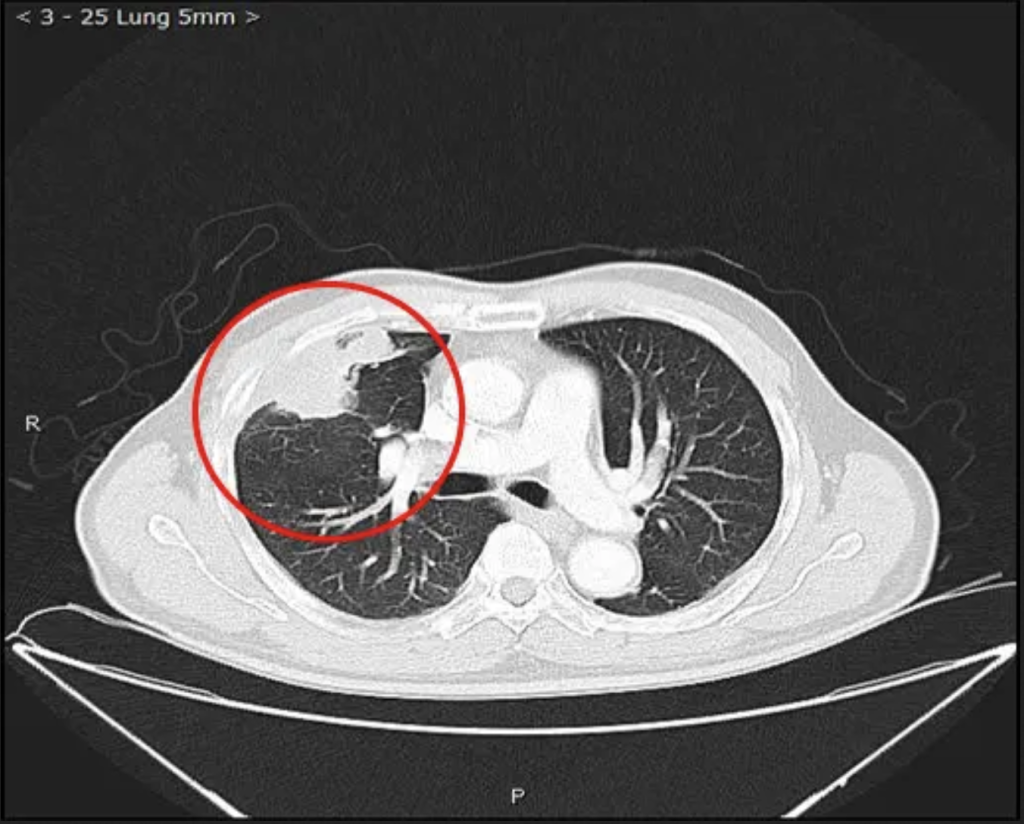
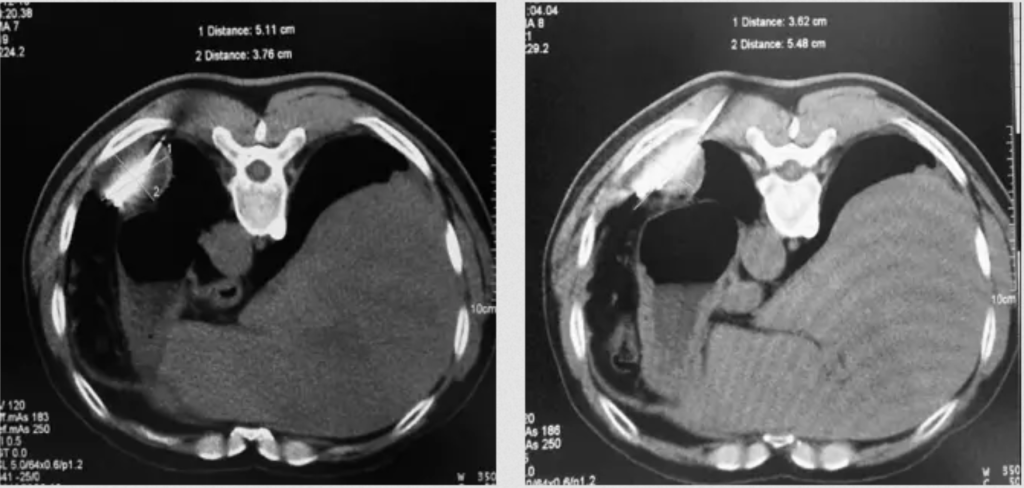
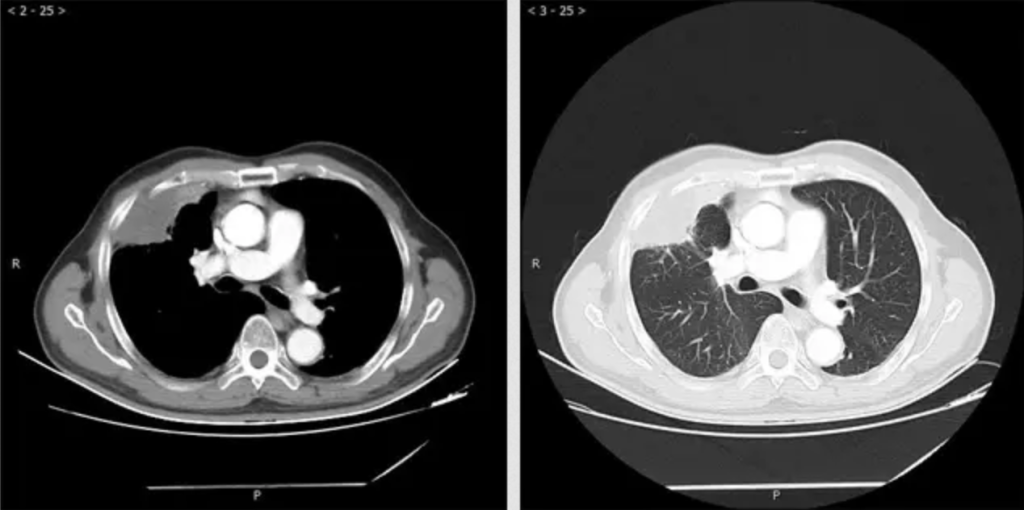
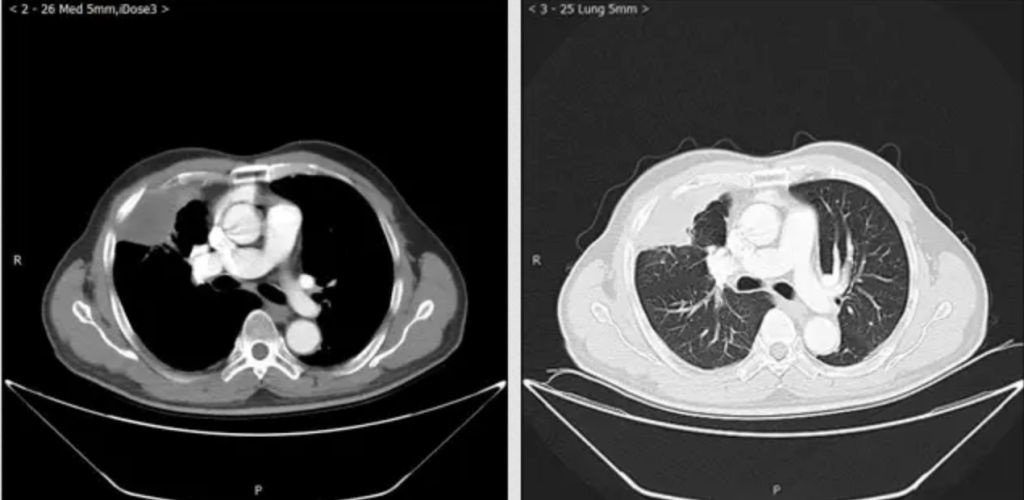
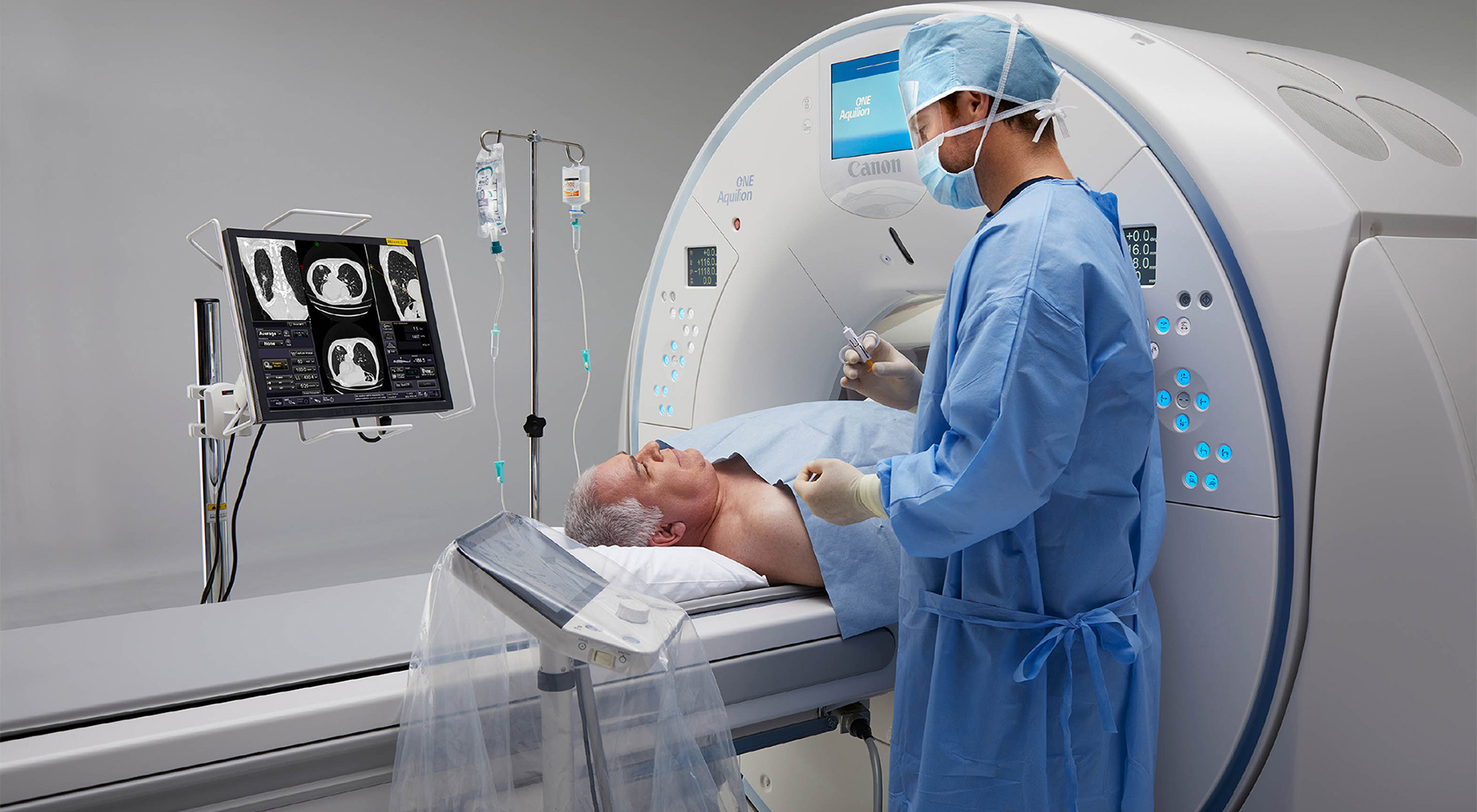
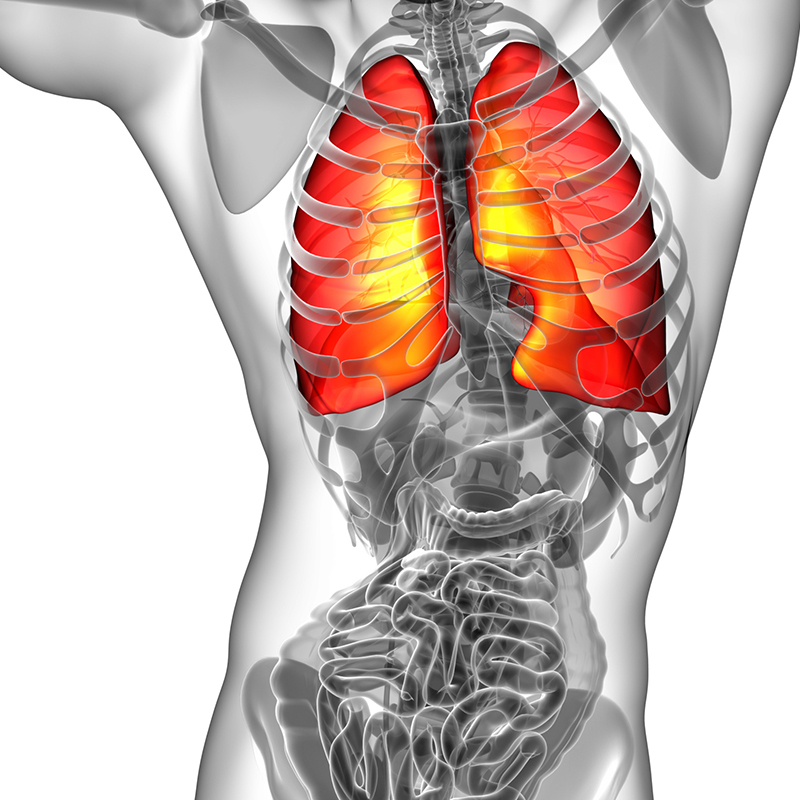
Clinical Applications for AI Epic™ Co-Ablation System- Lung Cancer
What is Cryotherapy for Lung Cancer? Lung cancer cryoablation is a minimally invasive therapeutic technique that offers a promising treatment option for select lung cancer cases. It utilizes extreme cold temperatures to destroy cancerous cells within the lung while sparing as much healthy tissue as possible. This approach is particularly suitable for patients who are not candidates for surgical resection or conventional therapies. During the procedure, a thin, needle-like probe is precisely inserted into the lung tumor. The probe delivers ultra-low temperatures, typically below -40°C, creating an ice ball that engulfs and destroys the cancer cells. Repeated freezing and thawing cycles induce cellular damage, ultimately resulting in targeted tumor necrosis.